I. Introduction

Biometric authentication has become increasingly prevalent in today’s society due to its enhanced security and ease of use. This evolving technology has introduced a new era of secure and efficient identification methods, with palm recognition standing out as a leading and innovative biometric solution.
A. The Rise of Biometric Authentication
In an increasingly digital and interconnected world, traditional authentication methods such as passwords and PINs are proving to be inadequate in safeguarding sensitive information. This has led to the rise of biometric authentication, which utilizes unique biological characteristics such as fingerprints, iris patterns, and facial features to verify individuals’ identities. Biometric authentication has gained popularity due to its ability to provide a seamless and secure means of access, addressing the limitations and vulnerabilities of traditional authentication methods.
B. The Emergence of Palm Recognition Technology
Palm recognition technology has emerged as a cutting-edge biometric solution, offering a secure and accurate method of identification based on the unique vein patterns and features of the human palm. Unlike other biometric modalities, it provides a stable and reliable form of authentication that is resistant to forgery or unauthorized access. As this technology continues to advance, its applications span across various sectors, including security, finance, healthcare, and more, positioning it as a transformative force in the realm of biometric authentication.
II. The Science Behind Palm Recognition
A. Unique Features of the Human Palm
The human palm carries an array of unique features that make it an exceptional candidate for biometric identification. Vein patterns, serve as the primary distinguishing characteristic. The vein layout in the palm creates a complex and individualized network that remains stable over time, making it an exceptionally reliable biometric identifier. Additionally, the palm’s surface topography, creases, and ridges further contribute to its distinctiveness. Unlike other biometric modalities, such as fingerprints, the palm’s vein pattern persists uninfluenced by external factors, ensuring long-term accuracy and consistency in recognition.
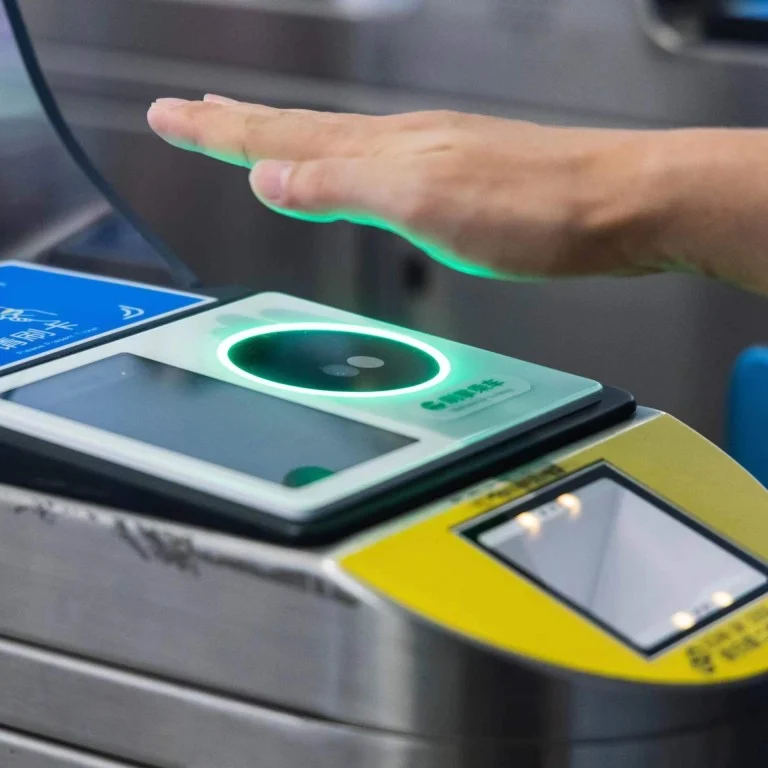

B. How Palm Recognition Works
Palm recognition technology operates through the capture and analysis of the unique vein pattern and features present in an individual’s palm. To initiate the process, near-infrared light is onto the palm’s surface, causing the hemoglobin in the veins to absorb the light and appear as dark patterns. A specialized camera then captures the reflection of the vein pattern, producing a digital image. This image is subsequently processed to isolate and extract the vein pattern, converting it into a digital template. This template is encrypted and securely stored within the system for comparison and authentication purposes. When an individual seeks access, their palm is scanned, and the captured vein pattern is matched against the stored template. If the patterns align, access is granted, providing a swift, accurate, and secure means of authentication.
III. Application of Palm Recognition
A. Secure Access Control and Authentication
Palm recognition technology has found widespread applications in the domain of secure access control and authentication. By leveraging the unique vein patterns and distinctive features of the human palm, this technology provides a highly secure and reliable method of verifying an individual’s identity. In various sectors such as corporate environments, government facilities, and healthcare institutions, palm recognition has been deployed to enhance the security of restricted areas, offering a seamless and efficient means of controlling access and safeguarding sensitive information. The integration of palm recognition into access control systems has significantly bolstered security measures and mitigated the risks associated with unauthorized entry, establishing it as an invaluable tool for ensuring secure access control and authentication.
B. Contactless Payments and Transactions
Palm recognition technology has also made notable strides in the realm of contactless payments and transactions. With the increasing emphasis on seamless and secure transaction methods, It has emerged as a pioneering solution for facilitating contactless payments. By capturing and analyzing the vein patterns of an individual’s palm, this technology enables swift and secure financial transactions without the need for physical contact or traditional payment methods. Its integration into payment systems has not only enhanced convenience for consumers but has also contributed to the advancement of secure and seamless financial transactions. The versatility of palm recognition technology in enabling secure, contactless interactions positions it as a pivotal driver in the evolution of payment and transaction mechanisms, catering to the growing demand for efficient and hygienic financial processes.
IV. Advantages of Palm Recognition
A. Enhanced Security and Accuracy

Palm recognition technology offers a significant advantage in the realm of biometric authentication through its unparalleled security and accuracy. The unique vascular structure of the human palm, characterized by intricate vein patterns, provides a highly secure method of identification that is exceedingly difficult to replicate or falsify. Unlike traditional authentication methods such as passwords or keycards, which are susceptible to breaches and unauthorized access, palm recognition ensures heightened security by leveraging the distinct biological features of the palm. This enhances the overall accuracy and reliability of authentication processes, mitigating the risks associated with identity fraud and unauthorized entry. Furthermore, the stability of palm vein patterns over an individual’s lifetime ensures long-term consistency and precision, cementing palm recognition as a premier solution for maintaining secure and accurate identification protocols.
B. Convenience and Hygiene
In addition to offering enhanced security, palm recognition technology introduces unparalleled convenience and hygiene to authentication processes. As the world increasingly prioritizes contactless interactions, palm recognition provides a hands-free method of identification, eliminating the need for physical contact with authentication devices. This not only enhances user convenience but also promotes a more hygienic environment, particularly in settings where the transmission of germs is a concern. The seamless and non-intrusive nature of palm recognition aligns with evolving societal expectations for efficient and hygienic authentication methods, positioning it as a preferred choice for addressing modern-day security and public health considerations.
V. Limitations and Challenges
A. Privacy Concerns and Ethical Implications
The deployment of palm recognition technology raises substantial privacy concerns and ethical implications, as it involves the capture and storage of individuals’ biometric data. The collection and utilization of such sensitive information have sparked debates surrounding data protection, individual privacy rights, and the potential for misuse or unauthorized access to biometric databases. These concerns are particularly pertinent in environments where palm recognition is employed for purposes beyond traditional access control, such as in commercial or consumer-facing applications. As such, it is imperative to establish robust privacy policies, consent frameworks, and secure data management protocols to safeguard the privacy and autonomy of individuals whose biometric data is being utilized for it.
B. Environmental and Technological Constraints
The widespread adoption of palm recognition technology also presents environmental and technological constraints that warrant attention. The production and deployment of palm recognition systems require significant technological infrastructure and resources, which may pose environmental sustainability challenges. The carbon footprint associated with the manufacturing and operation of biometric identification devices, as well as the potential e-waste generated from their disposal, necessitates a thoughtful approach to minimize the environmental impact of palm recognition technology. Additionally, the interoperability and integration of palm recognition systems with existing technological frameworks, particularly in diverse operational environments, may pose technical challenges that require careful consideration. Addressing these constraints involves assessing the environmental impact of palm recognition technology and devising sustainable practices, as well as prioritizing technological advancements that facilitate seamless integration and compatibility across diverse infrastructures.